Research
Projects
We have a number of funded and non-funded projects which are currently on-going.
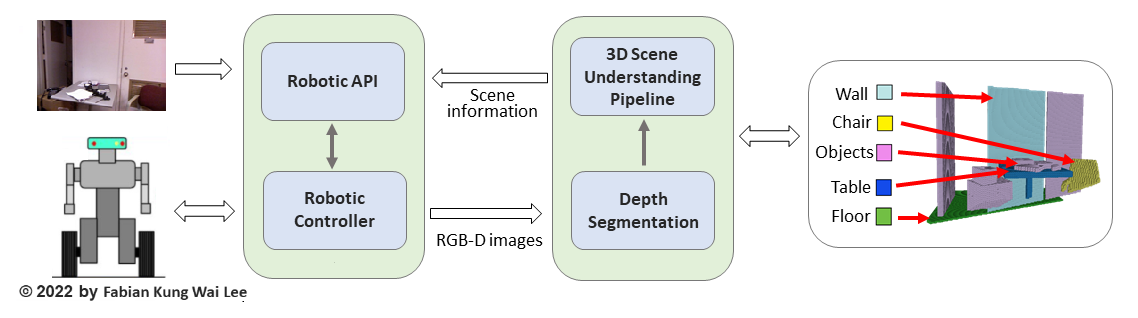
3D Semantic Scene Completion for Improving Robotic Scene Understanding
3D scene understanding is crucial for many AI applications, including robotic navigation. Due to limited field of view and sparse sensing, vision sensors suffer massive occlusion in cluttered environments, resulting in the captured scene representation being incomplete. To capacitate better 3D scene understanding, research on semantic scene completion (SSC), which aims to estimate the complete scene geometry and semantics simultaneously, is gaining much recent research interest. However, SSC is a highly challenging task and the performance of state-of-the-art methods still suffers in real-world data settings. To address the aforementioned limitations, this project aims to design novel SSC models that can perform 3D scene occupancy prediction and semantic scene segmentation simultaneously.
New Framework for Modeling Concurrent Low-light Image Enhancement and Object Classification with Deep Neural Networks
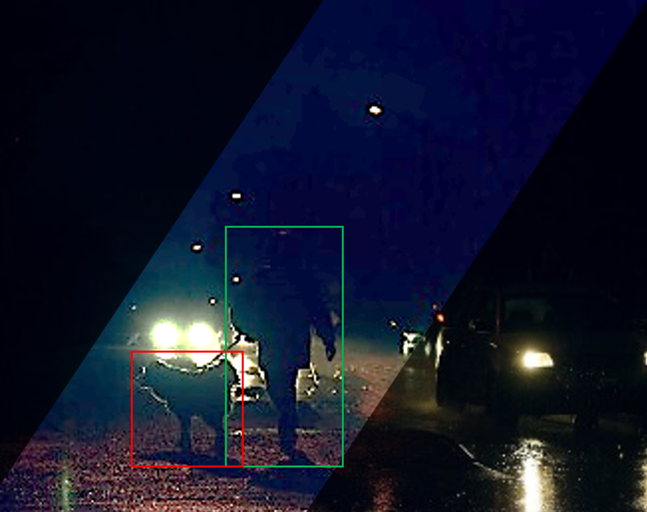
Object classification models based on deep learning has contributed to large scale deployments of intelligent vision systems for various practical applications. However, when such models are faced with low-light environments, their performance noticeably drop. This project aims to investigate and gain insights on the effects of low-light conditions on convolutional neural network models as well as to formulate a CNN architecture for simultaneous modelling of low-light image enhancement and object classification.
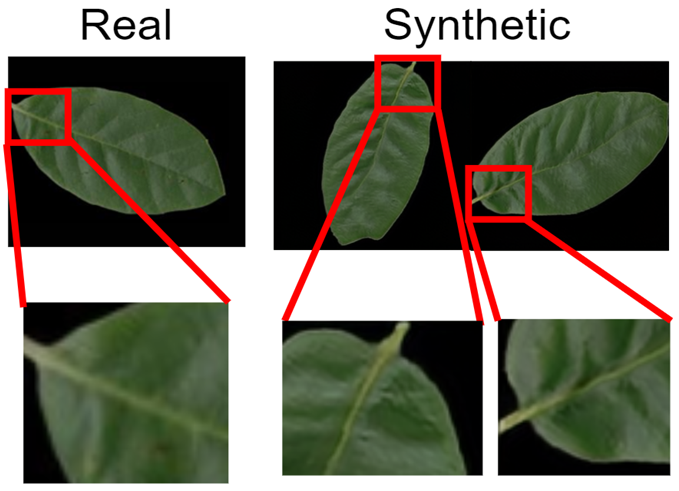
Filling in the taxonomic gap in botany through plant image synthesis
Plant taxonomy is a field of identification, description, and recording of plants in nature that supports various works related to the environment and agriculture. However, such work are highly reliant on distinctive expertise that are difficult to obtain. Therefore, automated plant identification from digital images has been in demand but yet they are heavily reliant on the training using large amounts of digital data that are not readily available. Hence, this project aims to investigate the use of synthesized image data as a solution to solve this data insufficiency problem in order to train effective plant classification models
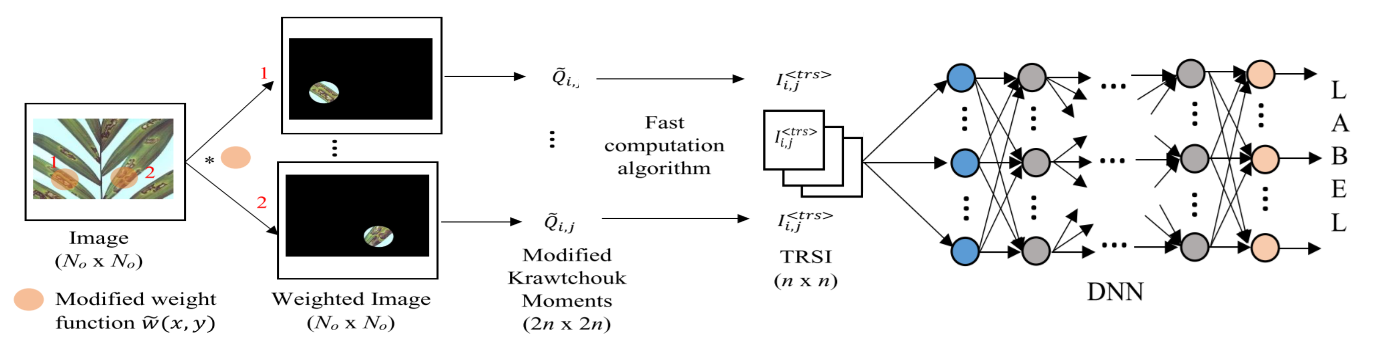
Deep learning with Krawtchouk moment for plant condition assessment
Agriculture sector often suffers great losses due to plant diseases. Image-based classification of plant diseases holds potential for early plant disease detection. However, automatic plant condition detection faces many challenges associated with large variations of visual symptoms, background and illumination. In this work, we proposed a moment-based Deep Neural Network (DNN) that utilizes our improved, high discriminative Krawtchouk moments for improving plant condition classification.
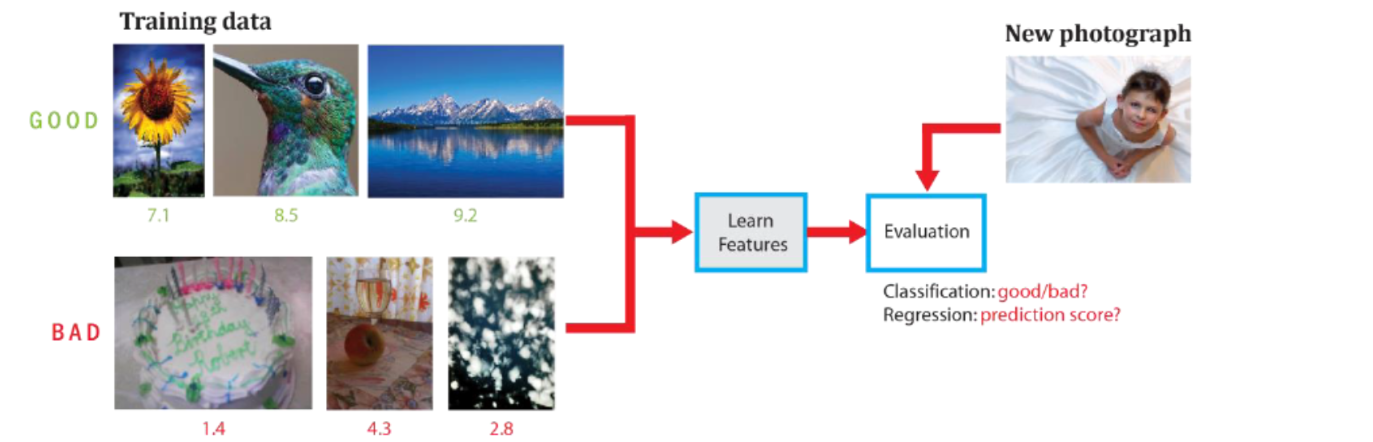
Large-scale Aesthetic Evaluation of Photographs (LAttE)
Image aesthetic evaluation is a research field which aims to design computationally-driven methods which can automatically rate or predict the perceived aesthetic quality of an image or photograph by learning from image content, photographic rules and other semantic information. We investigate how features can be learned in an unsupervised manner as opposed to traditional hand-crafted rules, and design new deep learning architectures to evaluate the aesthetic beauty of photographs.
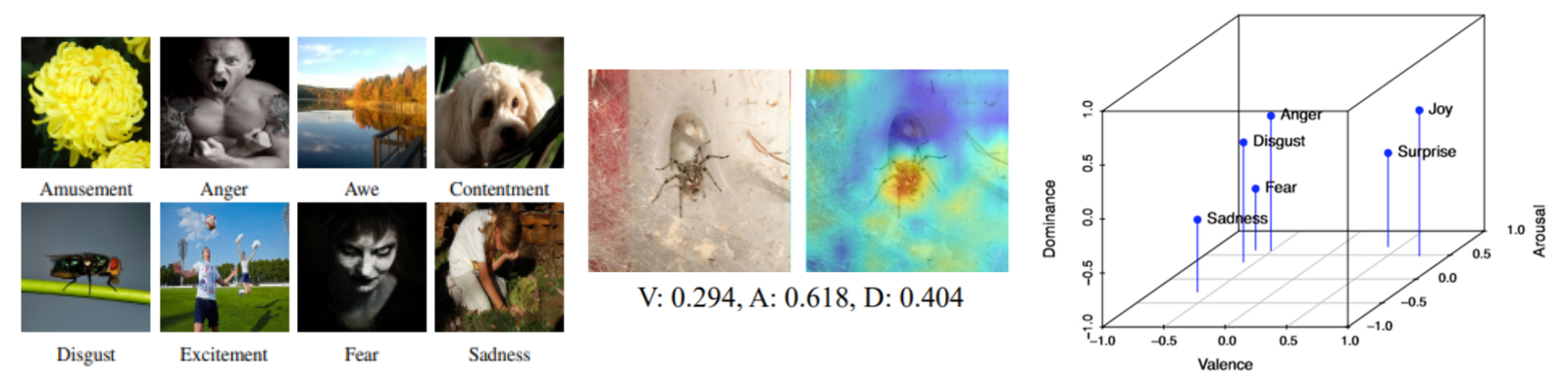
Modelling Image Emotion
Teaching machines to comprehend the nuances of emotion from photographs is a particularly challenging task. Emotion perception— naturally a subjective problem, is often simplified for computational purposes into categorical states or valence-arousal dimensional space, the latter being a lesser-explored problem in the literature. This project aims to study the relationship between an image and the emotion that it arouses, and to train deep learning models that can perform both categorical and dimensional emotion prediction from images.
Past Projects
Here’s some of our previous completed projects, which are still very much relevant today.
Generation of Polygonal Geometric Art
Automatic geometric abstraction which is a process of transforming an image into geometric art has widespread use in image editing and artistic synthesis. While existing methods yield unwanted distortions, are less subject-focused and even computationally expensive, we seek to design straightforward, non-learning algorithms which can support both triangle- and polygon-based abstraction without sacrificing on the semantics of subjects in the picture.
Facial Micro-Expression Analysis
A micro-expression is a brief and involuntary facial movement which reveals a genuine emotion that a person tries to hide. Psychologists have been studying facial micro-expressions since the 1960’s, computer scientists are now beginning to explore the possibility of spotting and identifying these micro-expressions using machine vision and learning algorithms; we aim to discover novel methods for doing so. This contemporary field of research has potential applications for clinical diagnosis of psychological conditions (autism and depression), criminal interrogation and lie detection. This project is in collaboration with institutions in UK and China.
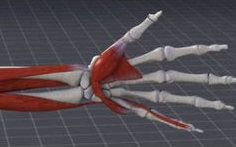
Computational 3D Model of Forearm Rotation
The mechanism that allows for human forearm rotation is still poorly understood. As a result, sub-optimal surgical treatment of fractured radius or ulna can lead to impaired forearm motion. We aim to develop a physically accurate 3D dynamic model of human forearm rotation from CT scan, with visualization of the model, the dynamic rotation and tensing of interosseous membrane. This is a project in collaboration with National University of Singapore (NUS) and Singapore General Hospital (SGH).
Action Recognition in Adverse Quality Surveillance (AQuaS)
Most state-of-the-art techniques for HAR have been designed to perform well under constrained and highly controlled conditions. However, these capabilities may not be easily replicable in real-world surveillance conditions (via devices such as CCTV or web cameras) where video quality may be naturally poor. We investigate new representations for recognizing human activities in adverse quality surveillance videos.
Aesthetics-driven Stereo Retargeting and Recomposition
With the recent availability of stereoscopic displays such as 3D monitor, 3D television and stereo camera phone, there is an increasing need for stereo image retargeting and recomposition techniques. Image retargeting aims to resize an image to fit different aspect ratios and sizes while image recomposition attempts to computationally modify the composition of an image to mimic a professional photo. We investigate new aesthetic-driven methods for retargeting and recomposition for stereo image pairs.
Long-term Video Surveillance (LoViS)
In a long-term period, video surveillance takes on a different perspective. Habitual behaviors of people or permanent changes to objects can be observed while anomalous “out-of-norm” variations can also be traced. We investigate how these variational patterns can be extracted over a long period of time to gain a high-level understanding of various factors at play.
Funding/Grants
External (Industry-funded)
- Comprehensive Steel Surface Defect Detection using Deep Neural Network, 2023-Ongoing, MMU-Aimflex Collaboration, PI: Wong Lai Kuan
- AI Technologies for Visual and Textual Media, 2020-2023 {:.marker}, MMU-Astro Collaboration, PI: Goh Hui Ngo
- Automatic Enhancement of Photographs for Improved Aesthetics Quality, 2020-2022, MMU-123RF Collaboration, PI: Wong Lai Kuan
- SHERLOCK: Video Analytics for Multi-Camera Long-term Surveillance in Smart Cities, 2016-2018, TM R&D Fund, PI: John See
External (Government/Institutional-funded)
- 3D Semantic Scene Completion via Novel Lightweight CNN-Transformer for Improving Robotic Scene Understanding, 2023-Ongoing, MMU-NTU-Heriot Watt-iRadar Collaboration, PI: Wong Lai Kuan
- Formulation of high discriminative discrete Krawtchouk moment invariants with Deep Neural Network learning model for plant condition assessment, 2021-Ongoing, MMU-Poladrone Collaboration, PI: Pee Chih Yang
- New Framework for Modeling Concurrent Low-light Image Enhancement and Object Classification with Deep Neural Networks, 2021-Ongoing, MMU-NCTU, Taiwan, PI: Loh Yuen Peng
- Player-Dependent Predictive Modeling for Automated Tactical Analysis of Badminton Videos, 2019-2022{:.marker}, MOHE FRGS Grant, PI: Ban Kar Weng
- Aesthetics-driven, Crop-and-Warp Image Recomposition Using Dual Learning Framework, 2019-2022{:.marker}, MOHE FRGS Grant, PI: Wong Lai Kuan
- Multi-scale Object Behaviour Recognition in Complex Videos, **2017-2019, One Belt One Road Initiative Young Scholar Exchange Grant, Co-PI: John See
- Novel Methods for Spotting and Recognition of Spontaneous Facial Micro-Expressions from Naturalistic Situations, 2016-2019, MOHE FRGS Grant, PI: John See
- Visual Recognition of Human Activities using Spatio-temporal Information for Low Quality Surveillance Video, 2014-2016, MOHE FRGS Grant, PI: John See
- Aesthetics-driven Stereoscopic Image Enhancement Algorithms for Better 3D Experience, 2013-2015, MOHE FRGS Grant, PI: Wong Lai Kuan
Internal
- Intelligent Breast Morphometry Prediction Framework for Peroperative Surgical Planning, 2022-2023, IR Fund, PI: Wong Lai Kuan
- Filling in the taxonomic gap in botany through plant image synthesis, 2021-2022, IR Fund, PI: Loh Yuen Peng
- High discriminative discrete Krawtchouk moment invariants, 2021-2022, IR Fund, PI: Pee Chih Yang
- Low-light Image Enhancement and Recognition, 2019-2020, Mini Fund, PI: Loh Yuen Peng
- Immersive Data Visualization using Virtual Reality, 2019-2020, Mini Fund, PI: Albert Quek
- Semi-supervised, Aesthetics-driven Image Recomposition Using Generative Adversarial Model, 2018-2019, Mini Fund, PI: Wong Lai Kuan
- Large-scale Computational Aesthetic Evaluation of Photographs using Deep Learning, 2016-2019, MMU-GRA Funding, PI: John See
- In Silico Modelling of Interosseous Membrane Behaviour in 3D Forearm Rotation, 2016-2018, MMU-GRA Funding, PI: Wong Lai Kuan
- Efficient Streaming of Real-time 360-degree Videos for Head Mounted Displays, 2017-2018, MMU R&D Capex Fund / MMU-GRA Funding, PI: Albert Quek
- Virtual Reality Fire Safety Intervention Program, 2015-2017, Mini Fund, Albert Quek